In the inventory management world, a debate arises between RFID identification and barcodes. As companies strive to optimize their data collection processes and improve inventory tracking capabilities, the decision between RFID and barcodes becomes increasingly crucial. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of each technology to determine which is most suitable for the needs of your organization.
The difference between Barcode and RFID
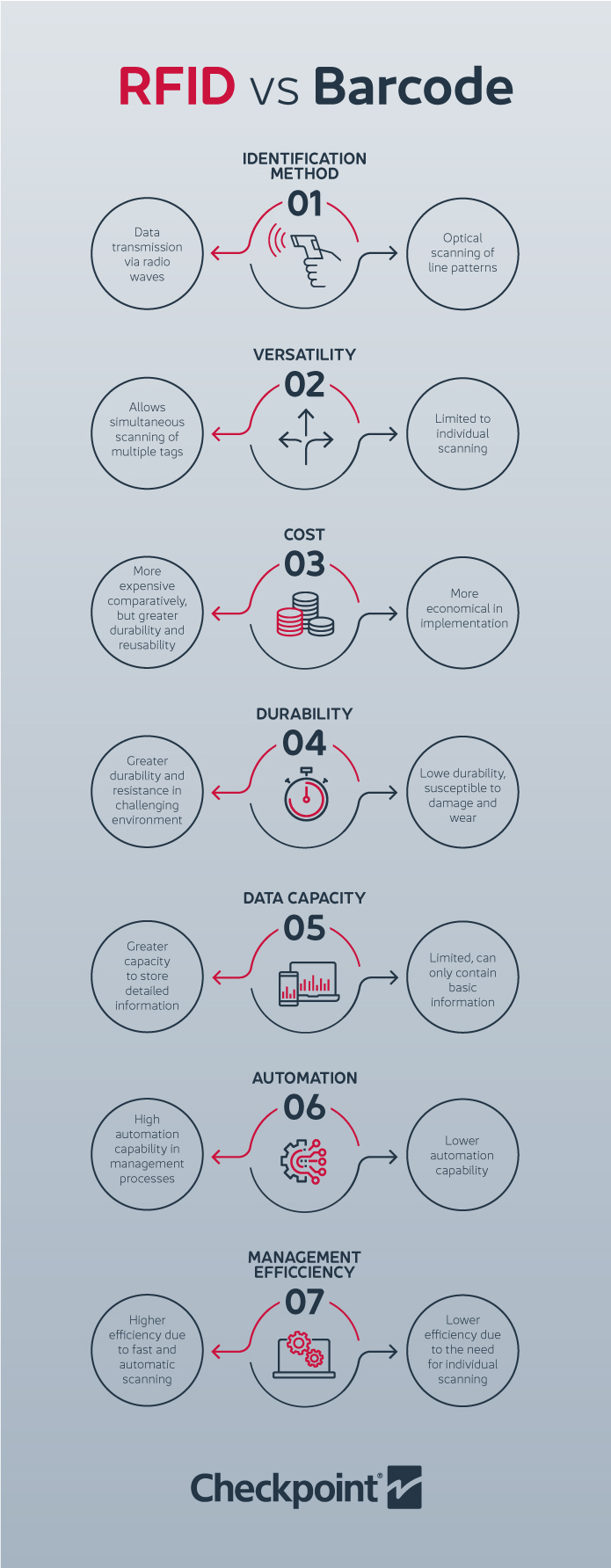
Both barcode technology and RFID serve to identify and track products, albeit through different mechanisms and characteristics.
Technology:
- Barcodes rely on printed patterns of black and white lines, individually scanned using optical scanners, and identified by a sequence of numbers.
- RFID uses radio waves to transmit data from chips to readers, enabling simultaneous scanning of multiple tags.
Strengths of barcodes:
- Cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for high-volume situations.
- Versatility due to ease of application and ability to print on various materials.
- Widely adopted as a standard technology across various sectors.
Differentiating features of RFID compared to barcodes:
- RFID allows for the definition of specific products and items through unique serial numbers, whereas barcodes only identify scanned products.
- An RFID label offers greater durability and reusability, suitable for challenging environments.
- Greater data capacity enables storing more detailed information for individual unit tracking and precise management.
In that sense, while barcodes are more economical and easier to implement, RFID technology offers higher speeds, durability, data capacity, and automation possibilities, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring high performance and advanced inventory management.
The advantages of RFID over barcodes
RFID technology enables rapid and efficient reading of multiple tags simultaneously to improve speed and accuracy in inventory management. Below, we detail the advantages of RFID vs barcodes:
- Speed: RFID significantly enhances inventory management by offering a notable improvement in speed and process efficiency. This improvement is achieved through the ability to scan multiple tags simultaneously, exponentially reducing manual workload and considerably optimizing operational effectiveness.
- Accuracy: RFID technology ensures high levels of accuracy in inventory tracking, with less susceptibility to human error compared to manual barcode scanning. In other words, RFID technology helps to avoid inventory discrepancies that occur with manual inventory, while also saving on labor hours for the team.
- Automation: RFID enables the automation of inventory management processes, leveraging comprehensive data to optimize operations, streamline workflows, and make objective decisions.
In conclusion, although both RFID and barcodes offer distinct advantages, the choice between them depends on the specific requirements and circumstances of your company. Factors such as budget, scalability, and operational preferences play a crucial role in determining the most suitable technology for inventory management.