Before delving into the intriguing lifecycle of an RFID tag, it's crucial to understand what is RFID. In summary, RFID technology emits radio frequency signals to interfere with wireless communication between a reader and a tag. The tag, equipped with a unique identifier for each product, responds to the radio frequency signals emitted by the reader, enabling rapid data transmission. This interaction provides real-time inventory information, facilitating informed decision-making and operational efficiency.
What is an RFID Tag
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags are the system's core component. These small yet intelligent labels efficiently store and transmit data through radio frequency signals. Despite their compact size, they possess a remarkable capacity for encoding vast amounts of information regarding a product's journey, from the supplier to the point of sale.
These labels not only store essential data but also incorporate advanced features such as cryptographic security, ensuring robust verification and authentication processes. RFID tags play a pivotal role in optimizing processes and improving overall efficiency across various industries.
How does an RFID tag work
An RFID tag interacts seamlessly with all components of the RFID system, including RFID antennas and software. Antennas emit electromagnetic signals that power and activate RFID tags, allowing them to wirelessly transmit their stored information. RFID readers capture these signals emitted by the tags and send them to the RFID management software for processing.
RFID software interprets and utilizes the data received from the tags and readers to provide real-time information about the location, status, and movement of tagged products. Additionally, the software can manage the RFID tag database, track inventory, generate performance reports, and automate logistical processes.
The synergy among the RFID tag, hardware and software is paramount for the efficient functioning of RFID systems across diverse applications, including inventory management, product security, asset tracking, and product authentication. These elements collectively form a comprehensive RFID ecosystem, furnishing visibility and oversight over products across the entire supply chain. A well-executed tagging initiative empowers brands to seamlessly integrate item-level inventory management, with the RFID label serving as the linchpin in every deployment.
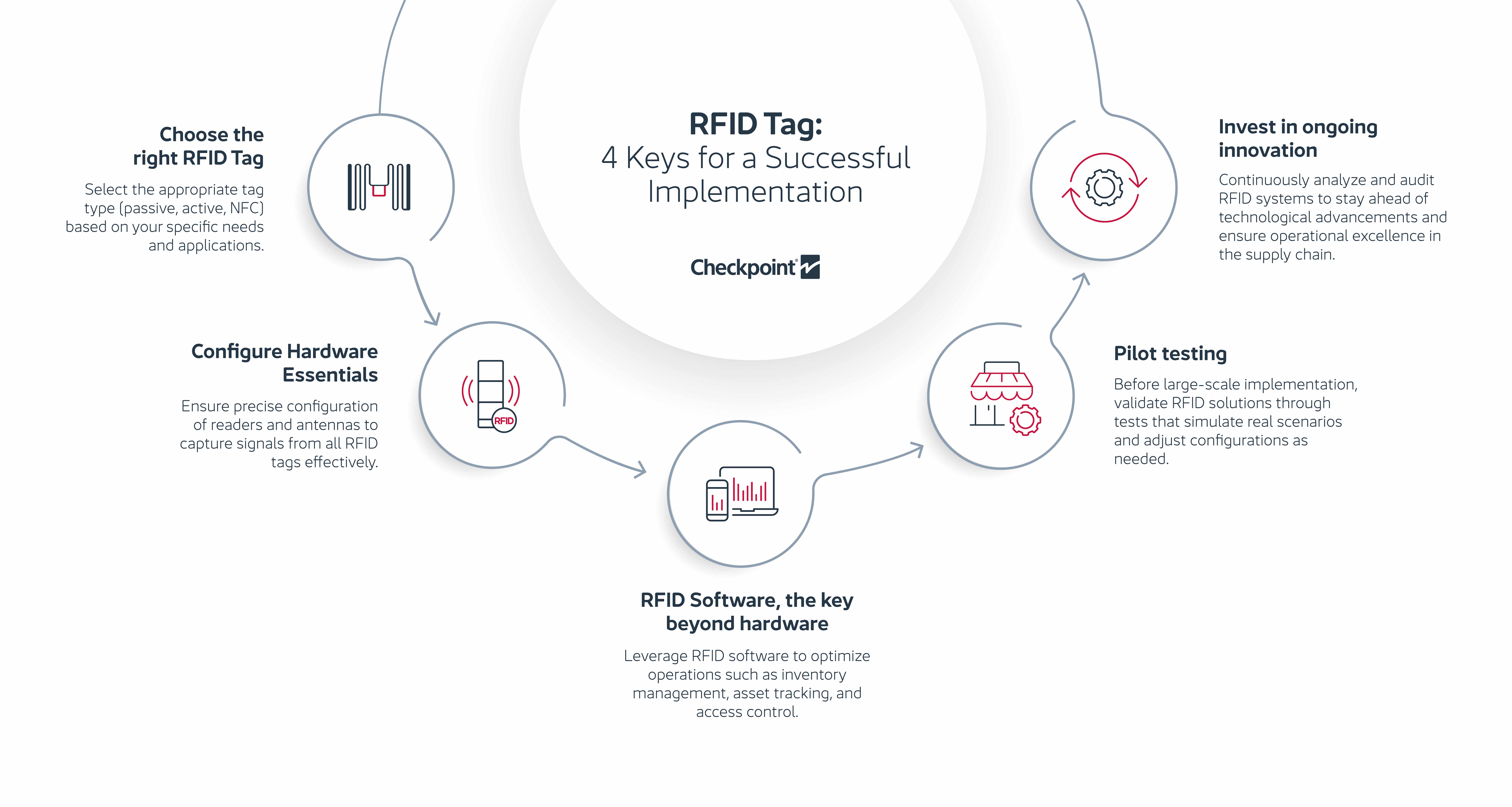
Choice of labels, the key to a successful implementation
The foundation of a successful RFID implementation begins with selecting appropriate tags tailored to the needs of each case. With many options available, from Active RFID tags to Passive ones, it is essential to consider which is most suitable for the product.
There are various types of tags, from passive ones that derive power from the reader's signal to active ones. Additionally, there are specialized tags for various applications, such as NFC tags for mobile payments or specific tags for asset tracking. At this stage of the process, it is important to assess where the tags will be located, as it allows us to identify which ones are most suitable depending on factors such as durability in environments like airports, incorporation into clothing for the fashion industry or traceability of liquid products, enabling improvements in stock management and distribution for wine, champagne, spirits and perfume companies.
Checkpoint Systems stands out in the passive UHF tag market, a specific type of RFID tag that offers a wide range of applications in inventory management, asset tracking, and access control. Passive UHF tags are highly effective and cost-efficient as they do not require an internal power source and can be read at relatively long distances, between 1 and 10 meters.
Examples of an innovative tag solution
RFID gives brands and retailers a game-changing opportunity to streamline operations and gain unprecedented insight into their inventory. However, the intricacies of implementing RFID in products, along with considerations for performance and memory usage, can pose challenges. This is where partnering with a reliable RFID technology provider becomes essential.
Consider the following scenarios to grasp the significance of having adaptable tags for diverse environments:
RFID Tag for Logistics and Supply Chain:
RFID tag is used to identify and track products throughout the supply chain. In environments where tag durability is required due to harsh conditions, solutions like the Tyfung inlay need to be implemented. Developed to offer the logistics sector a rugged RFID tag design with outstanding performance, it combines a long-read range (18-20 meters) with low sensitivity, making it ideal for use in industrial settings and throughout the supply chain, as well as in traditional retail applications.
RFID Tag for Food Industry:
Utilized to ensure product traceability across the entire production chain, this enables precise tracking of food items throughout the supply chain, facilitating quick identification and withdrawal of products in case of food safety issues. These tags must be specially designed to integrate into packaging without compromising the food safety of the products. That's why Checkpoint designs labels like Leveche, specifically tailored for labeling most items, as it is certified for use in microwaves and is food safe.
RFID Tag for Textile Industry:
RFID tag is used to improve Moreover, the value of the RFID tag is further amplified in today's context where omnichannel is a key driver for the best customer experience. It facilitates the integration of sales channels, ensuring consistent inventory management and a consistent customer experience, regardless of whether the customer is shopping online or in the store. In that connection, managing return shipments is not only labor-intensive but costly as well. Added to this are the complexities of maintaining accurate inventory levels, especially in the case of fashion items, which are subject to constant change. Thanks to RFID technology, stock can be managed in real time, avoiding the risk of having considerable overstock or understock, which could lead to significant financial losses.
The integration of embedded RFID solutions represents the future of RFID technology for retailers seeking innovation, as it allows for greater flexibility and branding options for RFID tags, opening the door to a range of additional benefits. This technology can take simple forms, such as being placed between the layers of cardboard of a price tag or hanging tag, to being included in woven and branded labels. With RFID tags no longer limited to just stickers and hang tags, brands can begin to leverage the benefits of RFID in loss prevention systems, automatic payment, frictionless shopping, smart mirrors, and many more applications.
In conclusion, implementing RFID technology effectively requires careful consideration of key factors such as tag selection, system integration, and environmental suitability. By embracing innovative tag solutions and leveraging the potential of RFID technology, businesses can unlock new levels of efficiency, visibility, and customer satisfaction across various industries.
