One of the main challenges companies face today is finding technologies that allow them to manage data, optimize processes, and improve user experience. In short, solutions that take them one step further in understanding customer needs in terms of cost, durability, and security.
Among the most widely used technologies for identifying, tracking, and authenticating products or information are RFID tags and QR codes. While both serve to store and share data, the way they operate and their applications differ significantly. In this article, we’ll explore what they are, their benefits, and their main differences.

What Is RFID Technology?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses radio waves to capture and store information from electronic tags that can be attached to or embedded in different products. These tags, known as RFID tags or sometimes referred to as an RFID code, contain electronic circuits that respond to signals sent by an RFID reader.
The main advantage of RFID over other identification systems, such as barcodes, is that it does not require direct line of sight to read or capture data, offering greater flexibility and efficiency.
The key components of this technology include:
- RFID Tags: Contain information about the product they are attached to. They can be passive, active, or semi-passive, depending on the type of power source they use.
- RFID Readers: Devices that emit radio signals to communicate with the tags and read the information they contain.
- Antennas: Facilitate the transmission and reception of signals between tags and readers.
- Management Software: Analyzes and manages the data collected by the readers.
What Are QR Codes?
QR codes are two-dimensional graphics that require line of sight to be read by cameras. They are more cost-effective, easy to implement with smartphones, and ideal for customer information or marketing purposes, although they are more vulnerable to wear and tear.
When scanned, they instantly provide access to the stored information, such as a website URL, phone number, email, or even more complex data like contact information or product details. To better understand the customer-facing applications of this technology, here’s a useful guide on How to Use QR Codes.
Key Differences: RFID vs. QR Codes
We analyse some of the main differences between RFID technology and QR codes.
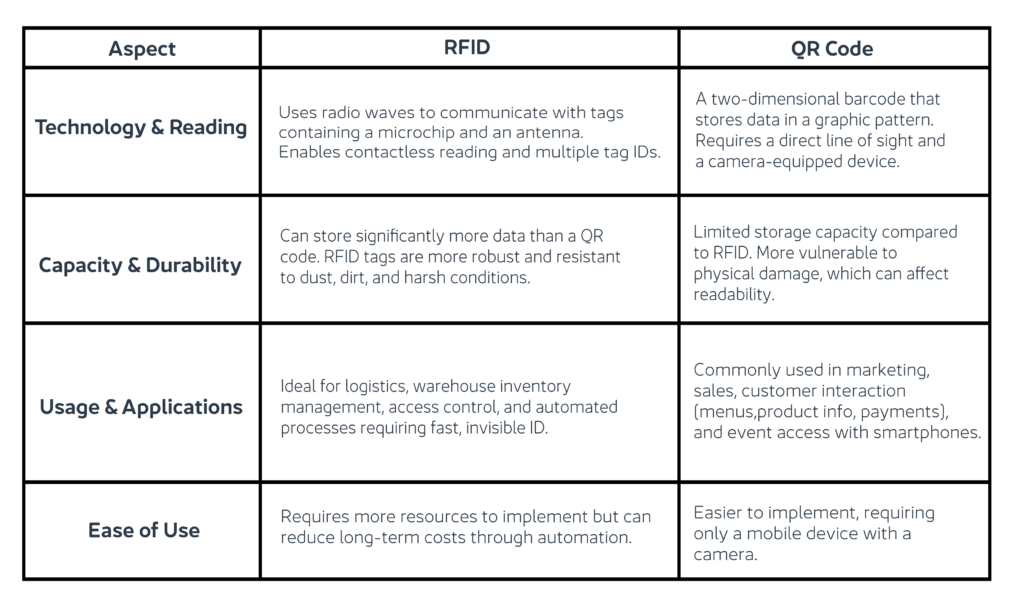
Technology and Reading
- RFID: Uses radio waves to communicate with tags containing a microchip and an antenna. It enables contactless reading and can identify multiple tags at once.
- QR code: A two-dimensional barcode that stores data in a graphic pattern. Requires direct line of sight and a camera-equipped reader (such as a smartphone) to scan.
Capacity and Durability
- RFID: Can store significantly more data than a QR code. RFID tags are also more robust and durable, resisting dust, dirt, and harsh environmental conditions.
- QR code: Has limited storage capacity compared to RFID. More susceptible to physical damage, which can affect readability in adverse conditions.
Usage and Applications
- RFID: Ideal for logistics and warehouse inventory management, access control, and automated processes where multiple objects must be identified quickly and efficiently, even when not visible.
- QR code: More focused on marketing, sales, and customer interaction, such as restaurant menus, product information, or payments. Also widely used for event access control thanks to its compatibility with smartphones.
Ease of Use
- RFID: Requires more resources to implement but can reduce long-term operational costs by automating processes.
- QR Code: Easier to implement, requiring only a mobile device with a camera.
Is There Real Convergence Between the Two?
While RFID and QR codes are often seen as competing technologies, in practice they tend to complement each other rather than replace one another.
For instance, in retail, RFID can streamline inventory management by enabling real-time tracking of products, while QR codes provide customers with product details, promotions, or interactive content. Similarly, in logistics, RFID supports large-scale automation, while QR codes simplify customer-facing processes such as package tracking.
The future points toward a hybrid approach, where both technologies coexist: RFID driving automation, security, and efficiency in backend processes, and QR codes enhancing accessibility and engagement in customer interactions.